The Nvidia Investment Opportunity
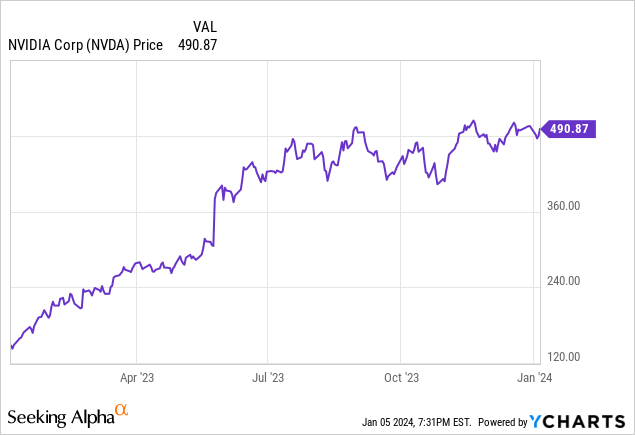
Nvidia Corporation’s (NASDAQ:NVDA) meteoric rise in 2023 has fueled misconceptions about its valuation. Contrary to popular belief, considering the company’s exceptional quality, formidable barriers to entry, and competitive advantages, it is poised for substantial earnings growth this year. Therefore, the notion that Nvidia is overvalued is unfounded. It is imperative to dispel these misconceptions and emphasize that Nvidia holds an alluring long-term value.
The First Misconception About Nvidia – The Alleged Overvaluation
At certain points in 2022, Nvidia traded at lofty multiples, yet these were warranted due to its robust earnings growth rates. As the stock surged, its forward P/E in the thirties and forward EV/EBITDA also in the thirties indicate that Nvidia is not overvalued in respect to its growth prospects and valuation.
The perception of Nvidia’s overvaluation due to its soaring stock price is flawed. The company’s remarkable competitive advantage and strong metrics underpin this surge. While some argue that Nvidia belongs to a cyclical industry, and its peak has been reached, evidence suggests otherwise.
Several companies, including Dell (DELL), Lenovo (OTCPK:LNVGY), and Hewlett Packard Enterprise Company (HPE), are still awaiting their H100 shipments, with wait times ranging from 36 to 52 weeks. This underscores the sustained demand for Nvidia’s products, preempting any significant earnings decline in the coming years.
Besides, Nvidia’s management has consistently demonstrated a keen aptitude for anticipating and aligning with future trends, such as the blockchain/crypto hype, LLM/generative AI hype, and positioning for full self-driving cars, fraud detection, and the Metaverse. These prospects hold the promise of substantial future revenue growth. Nvidia’s involvement in robotics with NVIDIA Isaac, in collaboration with Foxconn (OTCPK:FXCOF), presents another exciting opportunity.
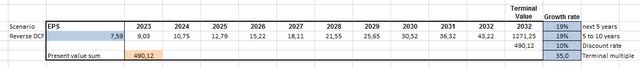
A reverse discounted cash flow (“DCF”) analysis, assuming a Diluted EPS TTM of $7.59, a 10% discount rate, and a terminal multiple of 35x, reveals that the stock’s current price implies an EPS growth rate of 19% over the next 10 years. This contrasts with Nvidia’s 3Y CAGR: 70.49%, 5Y CAGR: 32.33%, and 10Y CAGR: 44.34%, all well above the implied growth rate, suggesting that the stock may be undervalued.
The Second Misconception – It Is Just Hype, Nvidia Just Got Lucky And The Products Are Not That Awesome
Intel’s CEO Patrick Gelsinger’s claim that Nvidia “got extraordinarily lucky” due to the discontinuation of Intel’s Larrabee project is emblematic of Nvidia’s foresight and colossal competitive advantage, attesting to the quality of its management.
Within the GPU market, Nvidia and AMD reign supreme, with Nvidia’s inclination to lock customers into its ecosystem and innovations such as Raytracing, Upscaling DLSS, and G-Sync allowing it to dominate benchmarks and justify premium pricing. Nvidia’s supremacy in CUDA underscores its significant competitive advantage in the software domain. However, this moat is susceptible to possible threats.
In terms of maximum performance, the GeForce RTX 4090 currently stands unrivaled, with AMD trailing in second place, albeit by a significant margin. While AMD excels in the price/performance category, Intel’s presence in this market with the ARC A770 remains distant.
Anticipated developments, such as the RTX 5090’s potential switch to MCM design, foreshadow substantial leaps in performance, and Nvidia’s diversified portfolio beyond GPUs portrays its commitment to solving complex problems efficiently and expediently.
The Third Misconception – China
Speculation surrounding a decrease in sales in China due to geopolitical tensions is quelled by Nvidia’s adeptness in adjusting its product offerings, as evidenced by AMD’s release of the RX7900 GRE – Golden Rabbit Edition – with 16GB instead of 20GB of memory.
For instance, the GeForce RTX 4090D
An Investor’s Insight into Nvidia’s Future Growth
Nvidia, a leading player in the GPU market, is set to launch a GPU tailored specifically for the Chinese market. This strategic move will likely result in slightly less powerful versions tailored for China, facilitating broader market penetration. Despite this, the products are expected to gain traction, outperforming non-AMD or Nvidia alternatives.
Nvidia’s Impressive Financial Position
Nvidia boasts a robust financial standing with $18.3 billion in cash & ST Investments and a mere $9.8 billion in debt. The company comfortably covers its debt obligations, reflecting a solid balance sheet.
Furthermore, Nvidia has generated $14 billion in TTM free cash flow, surpassing its stock-based compensation of $3,293 billion, resulting in an SBC adjusted FCF of approximately $10.7 billion. This signals stringent capital management by Nvidia.
Nvidia’s Capital Allocation and ROIC
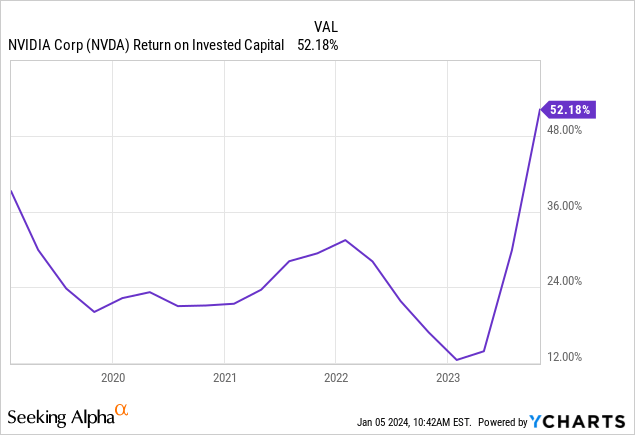
Nvidia’s return on invested capital (ROIC) has consistently exceeded 12% over the past 5 years, with an average of over 22%. Notably, the weighted average cost of capital (WACC) is estimated at 9%, resulting in a robust 43% ROIC – WACC spread, indicative of Nvidia’s strong performance and prudent financial management.
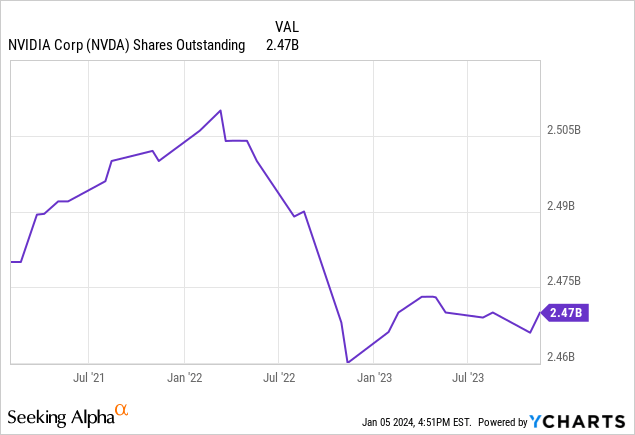
Moreover, Nvidia has effectively managed its stock-based compensation, leading to a decrease in outstanding shares over the last three years. The company is likely to deploy its FCF for further share buybacks, aligning management interests with those of shareholders.
Performance targets at Nvidia are based on non-GAAP operating income and total shareholder return, demonstrating a focus on shareholder value. Nonetheless, some investors may prefer unadjusted metrics for a more comprehensive evaluation.
Potential Risks and Evolution
Nvidia faces the risk of a potential downturn in the cycle, which could lead to a decline in revenue. However, the data center industry shows resilience, with major players like Microsoft (MSFT), Meta Platforms (META), and Amazon (AMZN) investing in new data centers and expressing interest in Nvidia’s upcoming H200 chips.
While the company operates in a lucrative sector, increased competition may pose a challenge, potentially resulting in margin pressures. AMD’s Mi300x has shown promise in benchmarks, and other competitors are designing chips tailored to specific needs, threatening Nvidia’s market share.
However, Nvidia is adapting and innovating, with initiatives like DGX Cloud, which simplifies AI adoption for customers. The company’s potential release of ARM CPUs and its involvement in powering devices like the Nintendo Switch signify a diversified approach to sustain its position in the market.
In addition, emerging computing approaches, such as quantum computing and analog iterative machines, present potential risks to Nvidia’s dominance. Competitors are also striving to disrupt Nvidia’s software moat, posing a threat to its market standing.
Outlook and Conclusion
Despite potential headwinds, Nvidia is poised for substantial growth in the coming years given the critical importance of its GPUs to customers. The company’s strategic significance is evidenced by trade restrictions imposed on its products. Looking ahead, both Nvidia and AMD are expected to strengthen their positions over the next five years, with Nvidia enjoying a relatively stronger market position.
In conclusion, while a temporary moderation in Nvidia’s growth may occur, the company’s solid long-term prospects indicate a favorable outlook for both its operations and stock performance.