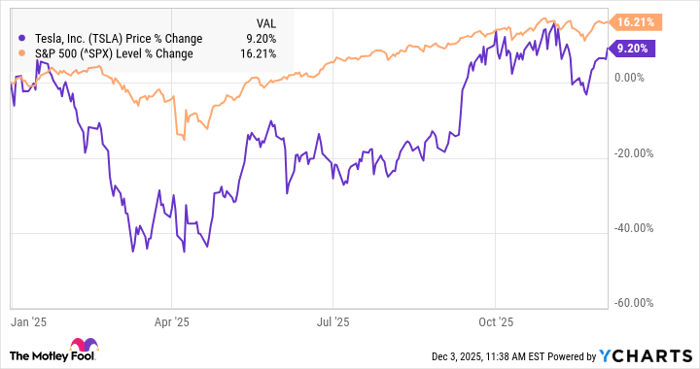
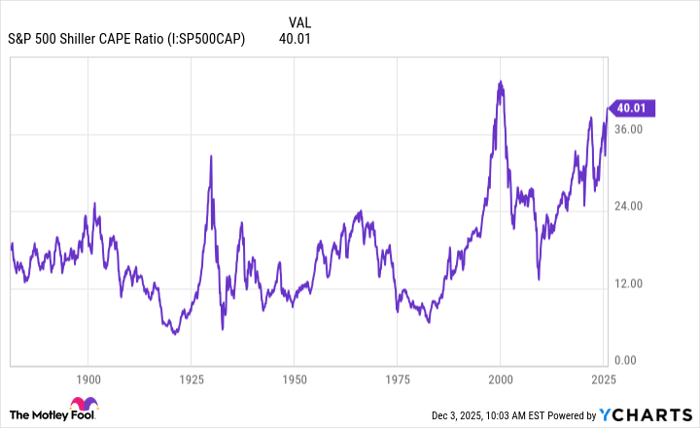
“`html
Understanding Qualified Institutional Buyers (QIBs) and Their Impact
A Qualified Institutional Buyer (QIB) is an institutional investor recognized for its expertise and financial capability in complex investment activities. This category includes entities such as insurance companies, investment firms, employee benefit plans, and select banks. These organizations must meet specific criteria established by federal securities regulators. The QIB designation is important as it opens the door to a broader range of investment opportunities, including private placements and securities not accessible to the general public. For more details, click here.
Consider consulting a financial advisor for investment guidance.
What Are Qualified Institutional Buyers (QIBs)?
QIBs are a unique group of investors identified by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) for their financial sophistication. Typically, to qualify as a QIB, an entity must be an institutional investor like an insurance company, investment firm, or pension fund, managing at least $100 million in securities. This classification enables QIBs to engage in private placements and other exclusive securities offerings, which are not available to the public. The premises of this provision assume that QIBs can manage their own risks without the need for extensive regulatory protections like state blue sky laws.
These investors play a crucial role in the financial markets. QIBs enhance liquidity and stability through their participation in private placements, thereby helping companies raise capital more efficiently. Since QIBs are deemed sophisticated, they are expected to assess the risks of these investments adequately, allowing issuers to navigate certain regulatory requirements more easily.
For companies, working with QIBs reduces regulatory burdens and attracts significant capital from these well-resourced investors. For QIBs, the benefits include early access to unique investment opportunities which may offer higher returns. However, these opportunities also carry increased risks, necessitating rigorous due diligence to ensure alignment with their financial objectives and risk tolerance levels.
Why Are QIBs Important for Investors?

Understanding QIBs clarifies their important role within financial markets. Their presence contributes to market liquidity and stability; large-scale transactions by QIBs can ensure smooth functioning during volatility. Additionally, these institutional investors usually maintain robust teams of investment professionals who rely on extensive research and analysis, fostering informed investment practices that enhance overall market resilience.
Moreover, QIBs distribute risk across various financial instruments and sectors, which helps mitigate adverse effects stemming from sudden economic fluctuations. These stabilizing influences ultimately benefit individual investors who depend on a reliable market for their investment strategies.
While QIBs operate on a significantly larger scale than individual investors, their investment choices can create opportunities for retail investors. The trends observed in QIB investments can indicate sector confidence, providing insights that retail investors can utilize for informed decision-making. The liquidity and stability fostered by QIBs can enhance the overall market environment, encouraging individual participation.
Exploring Rule 144A
Rule 144A is an SEC regulation that facilitates the resale of unregistered securities to QIBs. This rule was established to improve liquidity in the private placement securities market, allowing these securities to be traded more easily among large institutional players without the need for SEC registration. It is particularly advantageous for issuers looking to avoid the lengthy public offering registration processes, especially foreign firms aiming to access U.S. capital markets.
For investors, Rule 144A expands available investment avenues. It allows QIBs to diversify their portfolios with higher-yield securities not accessible in public markets. This flexibility appeals to institutional investors seeking to optimize their investment strategies.
Conclusion

Qualified Institutional Buyers are recognized by the SEC for their substantial financial expertise and portfolios. Typically, these entities include insurance companies, investment firms, and pension funds managing a minimum of $100 million in securities. The QIB designation provides access to private placements and lucrative investment opportunities that are not available to the broader public.
Tips for Retirement Savings
- A financial advisor can provide guidance tailored to your retirement goals. Finding one is easier than you think. Utilize SmartAsset’s free tool to connect with vetted financial advisors in your area, allowing you to have a complimentary introductory call to find the right fit. To start finding an advisor, take action now.
- Use SmartAsset’s 401(k) Calculator to understand how your employer-sponsored retirement plan can grow over time.
Photo credit: ©iStock.com/Prostock-Studio, ©iStock.com/kupicoo, ©iStock.com/gzorgz
The post Qualified Institutional Buyer (QIB): Definition and Who Qualifies appeared first on SmartReads by SmartAsset.
The views and opinions expressed herein are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect those of Nasdaq, Inc.
“`