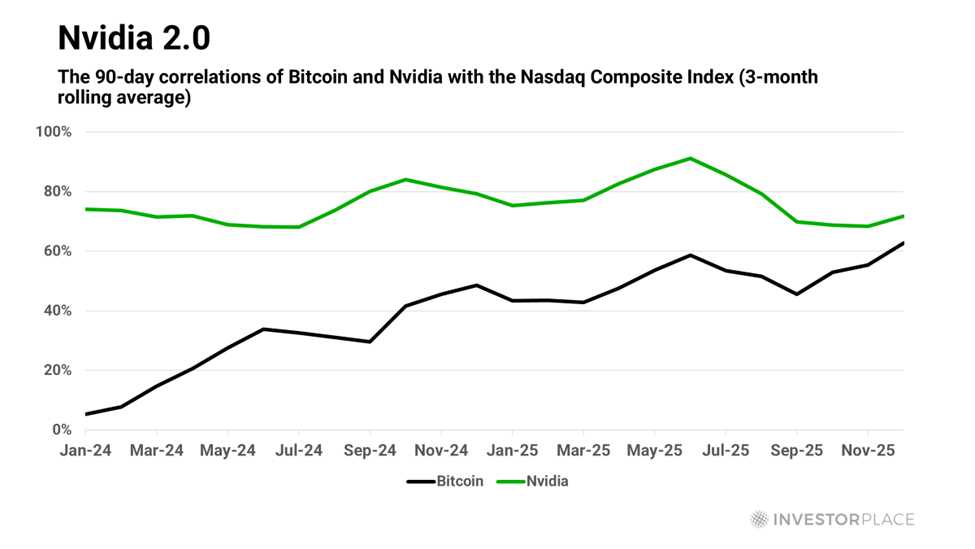
The Reserve Ratio: Key Insights into Its Impact on Banks and Consumers
The reserve ratio, established by central banks, determines the minimum reserves a commercial bank must hold compared to its deposits. These regulations ensure that banks maintain adequate liquidity to fulfill their obligations, thus protecting the financial system during crises. Additionally, central banks use the reserve ratio as a regulatory tool to influence the money supply, encouraging lending in slow economic times and controlling inflation during periods of rapid growth.
Working with a financial advisor can help you navigate loans and other financial choices affected by fluctuations in reserve rates.
Calculating the Reserve Ratio: What You Need to Know
The reserve ratio mandates that banks keep a specific percentage of their deposits in reserve. These reserves can be held in cash within the bank or as deposits with the central bank.
Central banks, like the Federal Reserve, enforce these requirements to ensure that financial institutions remain stable and liquid. This regulation helps banks access enough funds for customer withdrawals and other obligations.
If a bank runs out of funds and becomes insolvent, it risks failing to meet its obligations to depositors and creditors, potentially triggering a broader loss of confidence in the banking system.
The Economic Impact of the Reserve Ratio
Changes to the reserve ratio can significantly influence the economy’s money supply and overall activity.
When central banks decrease the reserve ratio, banks can lend more of their deposits, effectively increasing the money supply. This expansion can stimulate economic growth by encouraging consumer spending and business investment. However, a rapid increase in the money supply might also trigger inflation if it surpasses the economy’s growth rate.
Conversely, raising the reserve ratio requires banks to hold more funds in reserve and limits their ability to issue loans. This contraction can slow economic activity, helping to manage inflation, but it may also lead to job losses and reduced consumer spending. Therefore, central banks carefully adjust the reserve ratio to find a balance between growth and price stability.
Implications for Your Finances
Adjustments in the reserve ratio by the Federal Reserve can have several effects on your personal finances. A lower reserve ratio typically results in decreased interest rates, making loans more affordable and potentially boosting economic performance.
While a lower reserve ratio can enhance access to credit and lower borrowing costs, it may also mean that banks have less liquid cash to handle unexpected withdrawals. This situation can raise the risk of financial instability, affecting your financial security.
A higher reserve ratio forces banks to retain more deposits as reserves, limiting their lending capacity. This restriction can lead to increased interest rates and stricter lending requirements, making it harder for you to secure a loan.
Calculating a Bank’s Reserve Ratio
To determine a bank’s reserve ratio, divide its reserve balance by its total deposits. For instance, if a bank has $10 million in reserves and $100 million in deposits, the reserve ratio is 10%.
The Federal Reserve establishes minimum reserve ratios for U.S. banks, while allowing banks to hold more reserves if they choose. This calculation is important for monitoring the financial health and liquidity of banks.
The Bottom Line

The reserve ratio dictates how much of customer deposits banks must hold, either in their vaults or at the central bank. For consumers, this impacts interest rates and loan availability, including for mortgages. A higher reserve ratio restricts bank lending potential, leading to increased interest rates and tighter credit. In contrast, a lower reserve ratio can promote lending and encourage economic growth by unlocking more available funds.
Financial Planning Strategies
- Consulting a financial advisor can assist you in analyzing investments and managing your portfolio according to your financial objectives. Finding an advisor is straightforward; SmartAsset offers a free tool to connect you with up to three vetted financial advisors in your area, with free introductory calls to help you select the right fit.
- As interest rates fluctuate, SmartAsset’s free mortgage calculator can help you estimate monthly mortgage payments including taxes, fees, and insurance.
Photo credit: ©iStock.com/Yaroslav Olieinikov, ©iStock.com/Vadym Pastukh
The post What Is the Reserve Ratio? appeared first on SmartReads by SmartAsset.
The views and opinions expressed herein are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of Nasdaq, Inc.